| Component | FluidPort |
|---|---|
| Module | ARCHEAN_chemical |
| Mass | 1 kg |
| Size | 25 x 25 x 25 cm |
| Push/Pull Fluid | Accept Push/Pull |
Description
The fluid port is a device that allows for the suction or ejection of fluids.
This component is related to the pressurization of builds, please refer to the Pressurization page for more information.
When pulling in fluid, it will draw in the composition of the surrounding environment. For example, if it is submerged in water, it can fill a fluid tank with H2O, and if it is in the open air, it will draw in the composition of the atmosphere.
When pushing out fluid, it can purge fluid tanks of their contents.
Usage
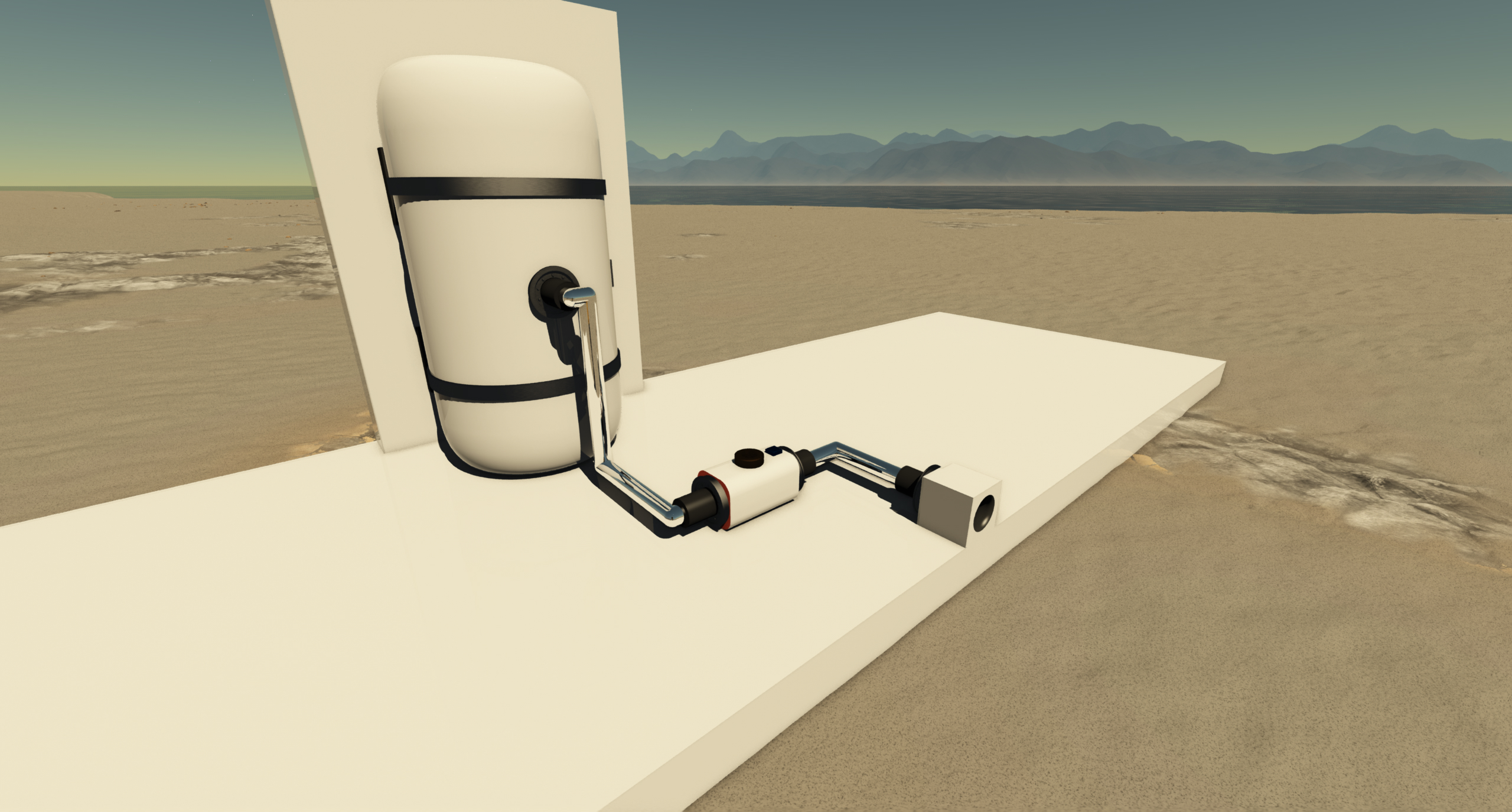
The fluid port acts as a bridge between a fluid container and the composition of the surrounding environment.
To operate, it needs to be connected to any component capable of holding or processing fluids.
Below is an example illustrating how it could be connected.

Flow Rate Limit
The Fluid Port has a maximum flow rate of 1.0 m³/s (volume-based, not mass-based).
Since the limit is volumetric, the actual mass transferred depends on the fluid density:
- Dense fluids (liquids like H2O, liquid O2) transfer more mass per second
- Light fluids (gases, high-altitude atmosphere) transfer less mass per second
- In vacuum (density = 0), nothing can be transferred
For example:
- Water (~1000 kg/m³): up to 1000 kg/s
- Sea-level air (~1.2 kg/m³): up to 1.2 kg/s
- High-altitude air (~0.4 kg/m³): up to 0.4 kg/s
Placement
When placing a Fluid Port, make sure the nozzle opening is oriented toward the area you want to interact with. You can mount it flush on a wall with the opening facing inward - as long as the nozzle points into the compartment, it will work correctly.
Information Window
Press V on a Fluid Port to display:
- Environment density (kg/m³): The density at the sampling point
- Environment Composition: The fluid composition by volume percentage
If the sampling point is inside a pressurized volume, it will show the volume's contents. Otherwise, it shows the ambient environment (atmosphere, water, etc.).